Cancer Treatment Types: Options, Categories, and What to Expect
At Health Talk, our mission is to help patients and families understand the different cancer treatment types available today. Advances in medicine mean that there are now more types of cancer therapy than ever before—ranging from traditional approaches like surgery for cancer and chemotherapy treatments for cancer to cutting-edge options such as CAR T cell therapy and targeted cancer therapy.
Whether you are newly diagnosed, supporting a loved one, or exploring cancer treatment options, this guide will walk you through the most common and emerging therapies, what to expect during treatment, and how to prepare.
Understanding Cancer Treatment
What is Cancer Treatment?
Cancer treatment includes various medical methods aimed at eliminating, managing, or slowing the progression of cancer cells. Depending on the type and stage of cancer, doctors may recommend one or more cancer treatment categories, either alone or in combination.
What Guides Treatment Decisions?
-
Cancer type and stage
-
Patient’s overall health
-
Tumor genetics (precision medicine)
-
Personal treatment goals
This is why choosing cancer treatment is a collaborative process between you and your care team.
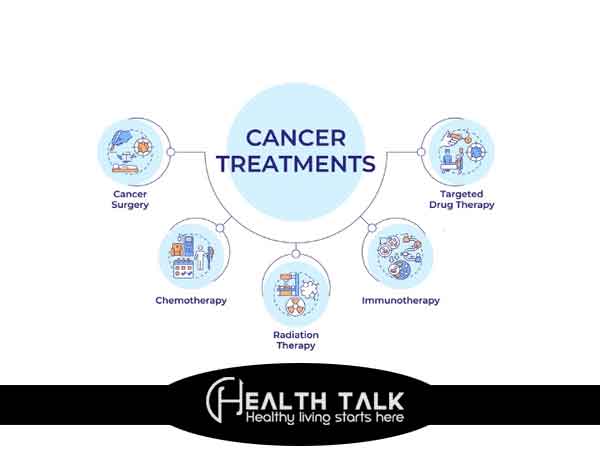
Main Types of Cancer Treatment
Surgery for Cancer
-
Open surgery
-
Minimally invasive techniques
-
Robotic-assisted surgery
Surgery is often combined with other therapies, such as surgery plus chemotherapy or radiation.
Radiation Therapy Types
Radiation uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. Common types of cancer therapy under this category include:
-
External beam radiation
-
Brachytherapy (internal radiation)
-
Advanced options like proton therapy and stereotactic radiosurgery
Chemotherapy Treatments for Cancer
Chemotherapy involves the use of strong medications to prevent cancer cells from multiplying and spreading. Treatment can be given orally, intravenously, or regionally (directly to the tumor site). While effective, it is often combined with chemotherapy and radiation for maximum results.
Hormone Therapy Cancer
For cancers driven by hormones—such as breast, prostate, or thyroid—hormone therapy blocks or lowers hormone levels in the body to slow cancer growth.
What is Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system, enabling it to detect and eliminate cancer cells more effectively. Immunotherapy cancer types include:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
-
Cancer vaccines
-
CAR T cell therapy, a breakthrough that engineers your immune cells to attack cancer
Targeted Therapy Explained
Unlike chemotherapy, targeted cancer therapy focuses on specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
Examples include:
-
Monoclonal antibodies
-
Antibody-drug conjugate cancer therapies
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Stem Cell (Bone Marrow) Transplant
Known as a hematopoietic stem cell transplant, this treatment replenishes blood-forming cells that are damaged or destroyed by intensive chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Ablation & Interventional Oncology Procedures
Minimally invasive options like cryoablation, radiofrequency ablation, and microwave ablation fall under interventional oncology procedures, offering alternatives for patients who may not tolerate major surgery.
Clinical Trials & Experimental Treatments
Patients may also access cutting-edge therapies through clinical trials, which test new drugs and combinations before they become widely available.
Combination & Multimodal Treatments
Doctors often recommend cancer treatment combinations for best results:
-
Surgery plus chemotherapy
-
Chemotherapy and radiation (chemoradiation)
-
Integrative care, including nutrition and exercise programs
This personalized approach ensures that treatment is tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Preparing for Cancer Treatment
Being ready—physically and emotionally—makes a difference. Here’s what to expect during cancer treatment:
-
Diagnostic tests and imaging
-
Treatment planning with your oncologist
-
Side effect management strategies
Preparing for cancer treatment also means asking the right questions, arranging support, and learning about possible financial resources.
Managing Side Effects & Recovery
Managing side effects of cancer treatment is an essential part of care. Side effects can be short-term or long-term:
-
Short-term: fatigue, nausea, hair loss
-
Long-term: fertility issues, neuropathy, organ effects
Coping with cancer therapies involves supportive care such as nutrition counseling, emotional support, and survivorship planning.
Choosing the Right Treatment Path
With so many cancer treatment options, making the right decision can feel overwhelming. Working with your care team ensures you receive evidence-based recommendations. Advances in personalized medicine mean treatments are more precise and effective than ever.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Seek immediate help if you experience:
-
Severe pain, fever, or signs
-
Shortness of breath or chest pain
-
Uncontrolled side effects
FAQs on Cancer Treatment Types
What is the most common type of cancer treatment?
Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain the most widely used cancer treatment categories.
Which treatment has the fewest side effects?
Targeted therapies and immunotherapies often have fewer systemic side effects compared to chemotherapy.
Can cancer be treated without chemotherapy?
Yes, many patients undergo surgery, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy without chemotherapy.
What are the latest advances?
Breakthroughs include CAR T cell therapy and antibody-drug conjugate cancer therapies, offering hope in hard-to-treat cancers.